Vintage shoes
Sam owns a small store that sells vintage shoes.
Business is going great, and one of her main issues is determining the price of new inventory as it comes in. Sam would like to create a machine learning model that automatically selects the best price using the historical performance.
Sam was a data scientist in a previous life, so she was surprised when she found some documentation recommending a new loss function: The Root Mean Squared Log Error (RMSLE.) This function seemed better than Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) for her use case.
Which of the following are some of the differences between RMSLE and RMSE?
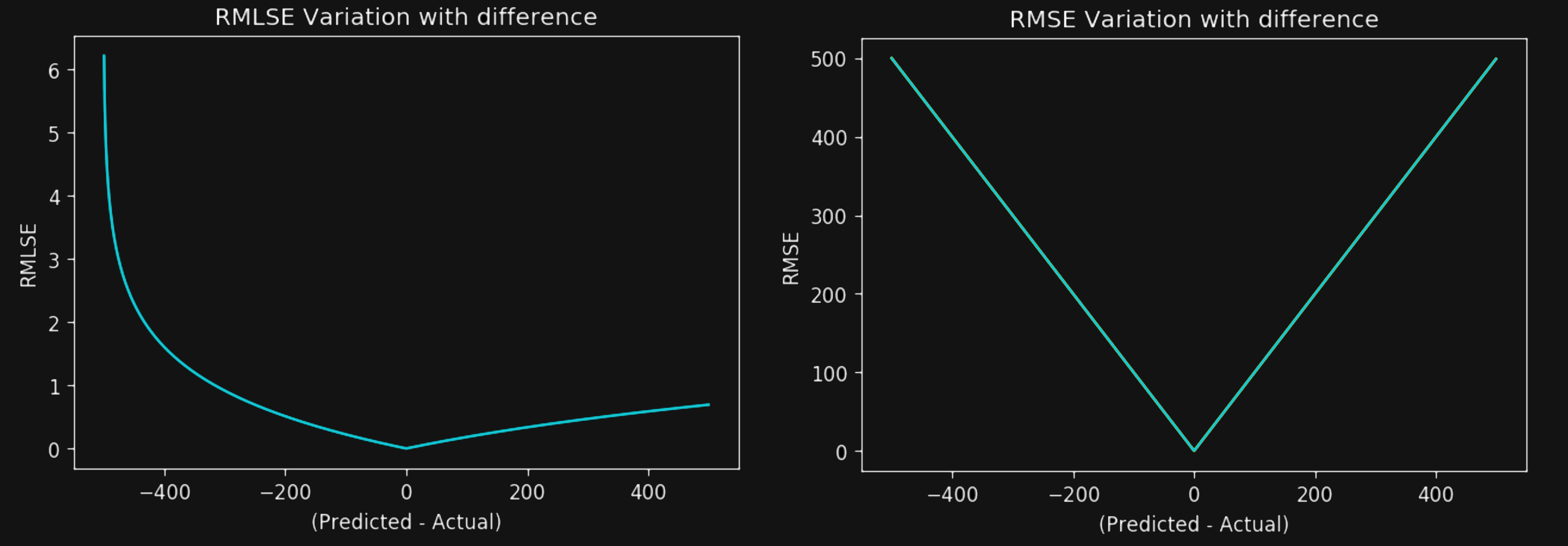
RMSLE penalizes coming under the actual value much more than coming above the actual value. On the other hand, RMSE penalizes both cases in the same way.
RMSLE is not sensitive to outliers as RMSE is. Whenever we have outliers, the result of RMSE can explode while RMSLE will scale down the outliers.
RMSLE measures the error by only focusing on the predicted value. On the other hand, RMSE uses the difference between the predicted and the actual value to compute the error.
RMSLE focuses on the relative error between two values. When using RMSLE, the scale of the error is not significant. On the other hand, the result of RMSE increases in magnitude if the error scale increases.